Linux Kernel ICMPv6
해당 포스트에서는 리눅스 커널의 ICMPv6 구현에 대해 설명합니다.
ICMPv6
ICMPv6 프로토콜은 IPv6을 위한 ICMP 프로토콜이다.
ICMPv6은 오류 처리와 진단 루틴 외에도 IPv6의 이웃 탐색(ND) 프로토콜과 멀티캐스트 리스너 탐색(MLD) 프로토콜에 사용된다.
ND 프로토콜은 IPv4 ARP 기능을 대체하고 강화했으며, MLD 프로토콜은 IPv4 IGMP에 대응된다.
ICMPv4의 ping과 traceroute와 마찬가지로, ping6과 traceroute6 유틸리티는 ICMPv6을 사용한다.
해당 챕터의 내용은 ICMPv4와 ARP의 내용을 파악하고 있다는 전제 하에 ICMPv6의 내용과 NDISC을 설명한다.
ICMPv6 초기화
ICMPv6의 초기화는 부팅 시 inet6_init() 함수에서 다음과 같이 수행한다.
static int __init inet6_init(void)
{
struct list_head *r;
int err = 0;
...
err = icmpv6_init();
if (err)
goto icmp_fail;
err = ndisc_init();
if (err)
goto ndisc_fail;
...
icmpv6_init() 함수에서는 다음과 같이 register_pernet_subsys(&icmpv6_sk_ops);로 초기화 및 종료 오퍼레이션을 등록하고, inet6_add_protocol(&icmpv6_protocol, IPPROTO_ICMPV6)로 프로토콜을 등록한다.
int __init icmpv6_init(void)
{
int err;
err = register_pernet_subsys(&icmpv6_sk_ops);
if (err < 0)
return err;
err = -EAGAIN;
if (inet6_add_protocol(&icmpv6_protocol, IPPROTO_ICMPV6) < 0)
goto fail;
err = inet6_register_icmp_sender(icmp6_send);
if (err)
goto sender_reg_err;
return 0;
sender_reg_err:
inet6_del_protocol(&icmpv6_protocol, IPPROTO_ICMPV6);
fail:
pr_err("Failed to register ICMP6 protocol\n");
unregister_pernet_subsys(&icmpv6_sk_ops);
return err;
}
등록한 오퍼레이션 및 프로토콜에 관련된 변수 및 함수는 다음과 같다.
static const struct inet6_protocol icmpv6_protocol = {
.handler = icmpv6_rcv,
.err_handler = icmpv6_err,
.flags = INET6_PROTO_NOPOLICY|INET6_PROTO_FINAL,
};
static int __net_init icmpv6_sk_init(struct net *net)
{
struct sock *sk;
int err, i;
net->ipv6.icmp_sk = alloc_percpu(struct sock *);
if (!net->ipv6.icmp_sk)
return -ENOMEM;
for_each_possible_cpu(i) {
err = inet_ctl_sock_create(&sk, PF_INET6,
SOCK_RAW, IPPROTO_ICMPV6, net);
if (err < 0) {
pr_err("Failed to initialize the ICMP6 control socket (err %d)\n",
err);
goto fail;
}
*per_cpu_ptr(net->ipv6.icmp_sk, i) = sk;
/* Enough space for 2 64K ICMP packets, including
* sk_buff struct overhead.
*/
sk->sk_sndbuf = 2 * SKB_TRUESIZE(64 * 1024);
}
return 0;
fail:
icmpv6_sk_exit(net);
return err;
}
static struct pernet_operations icmpv6_sk_ops = {
.init = icmpv6_sk_init,
.exit = icmpv6_sk_exit,
};
즉, CPU 별로 ICMPv6 소켓을 생성하여 보관하고, ICMPv6 패킷 핸들러로 icmpv6_rcv() 함수를 사용한다.
ICMPv6 헤더
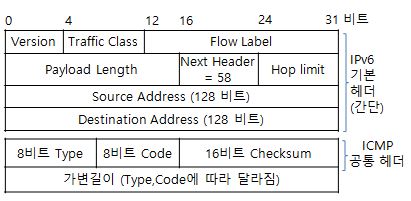
ICMPv6 헤더는 icmp6hdr 구조체로 표현한다.
struct icmp6hdr {
__u8 icmp6_type;
__u8 icmp6_code;
__sum16 icmp6_cksum;
...
};
생략된 부분에는 ICMPv6의 다양한 페이로드 타입을 지원하기 위하여 여러 타입을 union으로 묶어두고 있다.
icmp6_type 필드의 상위 비트가 0이면(0 ~ 127 값) 오류 메시지를 나타내고, 상위 비트가 1(128 ~ 255 값)이면 정보 메시지를 나타낸다.
해당 필드에 할당될 수 있는 값들은 다음과 같다.
// error message
#define ICMPV6_DEST_UNREACH 1
#define ICMPV6_PKT_TOOBIG 2
#define ICMPV6_TIME_EXCEED 3
#define ICMPV6_PARAMPROB 4
// info message
#define ICMPV6_ECHO_REQUEST 128
#define ICMPV6_ECHO_REPLY 129
#define ICMPV6_MGM_QUERY 130
#define ICMPV6_MGM_REPORT 131
#define ICMPV6_MGM_REDUCTION 132
#define ICMPV6_NI_QUERY 139
#define ICMPV6_NI_REPLY 140
#define ICMPV6_MLD2_REPORT 143
#define ICMPV6_DHAAD_REQUEST 144
#define ICMPV6_DHAAD_REPLY 145
#define ICMPV6_MOBILE_PREFIX_SOL 146
#define ICMPV6_MOBILE_PREFIX_ADV 147
#define ICMPV6_MRDISC_ADV 151
#define NDISC_ROUTER_SOLICITATION 133
#define NDISC_ROUTER_ADVERTISEMENT 134
#define NDISC_NEIGHBOUR_SOLICITATION 135
#define NDISC_NEIGHBOUR_ADVERTISEMENT 136
#define NDISC_REDIRECT 137
ICMPv6 메시지 수신
다음 그림은 ICMPv6 메시지의 Rx 경로를 나타낸다.
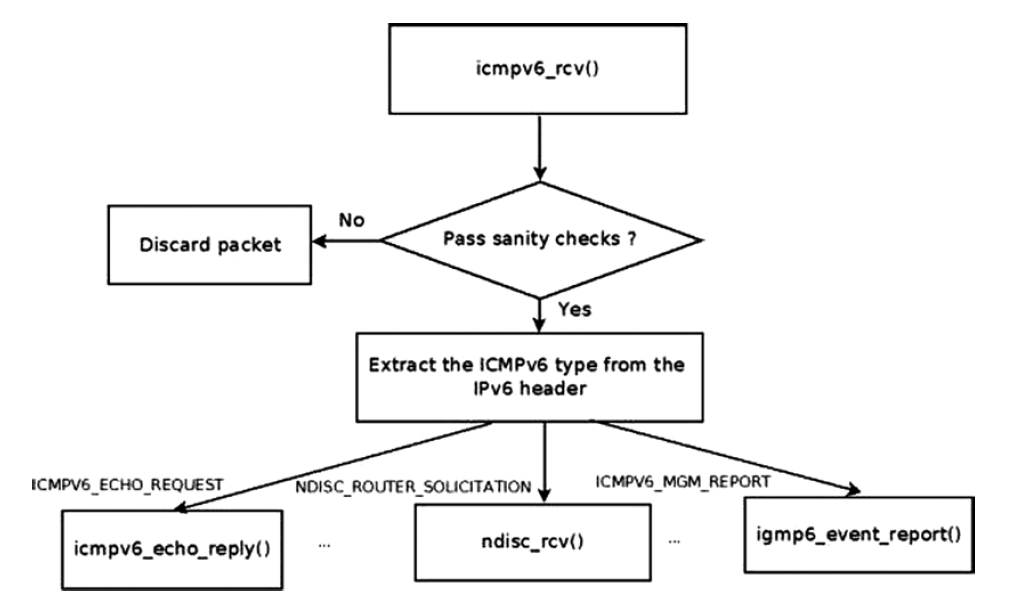
icmpv6_rcv() 함수의 정의는 다음과 같다.
static int icmpv6_rcv(struct sk_buff *skb)
{
struct net *net = dev_net(skb->dev);
struct net_device *dev = icmp6_dev(skb);
struct inet6_dev *idev = __in6_dev_get(dev);
const struct in6_addr *saddr, *daddr;
struct icmp6hdr *hdr;
u8 type;
bool success = false;
if (!xfrm6_policy_check(NULL, XFRM_POLICY_IN, skb)) {
struct sec_path *sp = skb_sec_path(skb);
int nh;
if (!(sp && sp->xvec[sp->len - 1]->props.flags &
XFRM_STATE_ICMP))
goto drop_no_count;
if (!pskb_may_pull(skb, sizeof(*hdr) + sizeof(struct ipv6hdr)))
goto drop_no_count;
nh = skb_network_offset(skb);
skb_set_network_header(skb, sizeof(*hdr));
if (!xfrm6_policy_check_reverse(NULL, XFRM_POLICY_IN, skb))
goto drop_no_count;
skb_set_network_header(skb, nh);
}
__ICMP6_INC_STATS(dev_net(dev), idev, ICMP6_MIB_INMSGS);
saddr = &ipv6_hdr(skb)->saddr;
daddr = &ipv6_hdr(skb)->daddr;
if (skb_checksum_validate(skb, IPPROTO_ICMPV6, ip6_compute_pseudo)) {
net_dbg_ratelimited("ICMPv6 checksum failed [%pI6c > %pI6c]\n",
saddr, daddr);
goto csum_error;
}
if (!pskb_pull(skb, sizeof(*hdr)))
goto discard_it;
hdr = icmp6_hdr(skb);
type = hdr->icmp6_type;
ICMP6MSGIN_INC_STATS(dev_net(dev), idev, type);
switch (type) {
case ICMPV6_ECHO_REQUEST:
if (!net->ipv6.sysctl.icmpv6_echo_ignore_all)
icmpv6_echo_reply(skb);
break;
case ICMPV6_ECHO_REPLY:
success = ping_rcv(skb);
break;
case ICMPV6_EXT_ECHO_REPLY:
success = ping_rcv(skb);
break;
case ICMPV6_PKT_TOOBIG:
/* BUGGG_FUTURE: if packet contains rthdr, we cannot update
standard destination cache. Seems, only "advanced"
destination cache will allow to solve this problem
--ANK (980726)
*/
if (!pskb_may_pull(skb, sizeof(struct ipv6hdr)))
goto discard_it;
hdr = icmp6_hdr(skb);
/* to notify */
fallthrough;
case ICMPV6_DEST_UNREACH:
case ICMPV6_TIME_EXCEED:
case ICMPV6_PARAMPROB:
icmpv6_notify(skb, type, hdr->icmp6_code, hdr->icmp6_mtu);
break;
case NDISC_ROUTER_SOLICITATION:
case NDISC_ROUTER_ADVERTISEMENT:
case NDISC_NEIGHBOUR_SOLICITATION:
case NDISC_NEIGHBOUR_ADVERTISEMENT:
case NDISC_REDIRECT:
ndisc_rcv(skb);
break;
case ICMPV6_MGM_QUERY:
igmp6_event_query(skb);
return 0;
case ICMPV6_MGM_REPORT:
igmp6_event_report(skb);
return 0;
case ICMPV6_MGM_REDUCTION:
case ICMPV6_NI_QUERY:
case ICMPV6_NI_REPLY:
case ICMPV6_MLD2_REPORT:
case ICMPV6_DHAAD_REQUEST:
case ICMPV6_DHAAD_REPLY:
case ICMPV6_MOBILE_PREFIX_SOL:
case ICMPV6_MOBILE_PREFIX_ADV:
break;
default:
/* informational */
if (type & ICMPV6_INFOMSG_MASK)
break;
net_dbg_ratelimited("icmpv6: msg of unknown type [%pI6c > %pI6c]\n",
saddr, daddr);
/*
* error of unknown type.
* must pass to upper level
*/
icmpv6_notify(skb, type, hdr->icmp6_code, hdr->icmp6_mtu);
}
/* until the v6 path can be better sorted assume failure and
* preserve the status quo behaviour for the rest of the paths to here
*/
if (success)
consume_skb(skb);
else
kfree_skb(skb);
return 0;
csum_error:
__ICMP6_INC_STATS(dev_net(dev), idev, ICMP6_MIB_CSUMERRORS);
discard_it:
__ICMP6_INC_STATS(dev_net(dev), idev, ICMP6_MIB_INERRORS);
drop_no_count:
kfree_skb(skb);
return 0;
}
switch(type) statement 이후로 메시지 타입에 따라 그에 맞는 핸들러를 호출한다.
알 수 없는 타입의 메시지를 수신하는 경우 icmpv6_notify(skb, type, hdr->icmp6_code, hdr->icmp6_mtu); 라인으로 오류를 알린다.
ICMPv6 메시지 송신
ICMPv6 주요 송신 함수는 icmpv6_send() 함수이다.
예외적으로 ICMPV6_ECHO_REQUEST 메시지에 대한 응답은 icmp_echo_reply() 함수로 처리한다.
icmpv6_send() 함수는 __icmpv6_send() 함수의 래퍼인데, 이 함수는 결국 icmp6_send() 함수를 호출한다.
icmp6_send() 함수와 icmp_echo_reply() 함수 모두 결국 ip6_append_data() 함수와 ip6_flush_pending_frames() 함수 혹은 icmpv6_push_pending_frames() 함수를 호출하여 IPv6 계층으로 전달한다.
다음은 ICMPv6 메시지 송신의 몇 가지 예시이다.
홉 제한 초과
ip6_forward() 함수에서는 포워딩 시 hop_limit 값을 1 감소한다.
hop_limit 값이 0이 되면 ICMPV6_TIME_EXCEED/ICMPV6_EXC_HOPLIMIT 메시지를 회신한다.
if (hdr->hop_limit <= 1) {
icmpv6_send(skb, ICMPV6_TIME_EXCEED, ICMPV6_EXC_HOPLIMIT, 0);
__IP6_INC_STATS(net, idev, IPSTATS_MIB_INHDRERRORS);
kfree_skb(skb);
return -ETIMEDOUT;
}
단편화 필요
ip6_forward() 함수에서 패킷의 크기가 MTU보다 크고 SKB의 local_df 비트가 설정돼 있지 않으면 패킷은 drop되고 ICMPv6 오류 메시지를 회신한다.
IPv6에서 라우터는 단편화를 진행하지 않기 때문에 패킷의 크기가 MTU보다 크다면 단편화를 수행하지 않고 ICMPV6_PKT_TOOBIG 메시지를 회신한다.
if (ip6_pkt_too_big(skb, mtu)) {
/* Again, force OUTPUT device used as source address */
skb->dev = dst->dev;
icmpv6_send(skb, ICMPV6_PKT_TOOBIG, 0, mtu);
__IP6_INC_STATS(net, idev, IPSTATS_MIB_INTOOBIGERRORS);
__IP6_INC_STATS(net, ip6_dst_idev(dst),
IPSTATS_MIB_FRAGFAILS);
kfree_skb(skb);
return -EMSGSIZE;
}
목적지/포트 연결할 수 없음
UDPv6 패킷을 수신하면 해당 포트에 일치하는 UDPv6 소켓을 찾는다.
일치하는 소켓을 찾지 못하면 체크섬을 확인하고, 체크섬이 잘못됐으면 패킷을 drop한다.
체크섬이 정확하면 통계를 업데이트하고 ICMPV6_DEST_UNREACH/ICMPV6_PORT_UNREACH 메시지를 회신한다.
int __udp6_lib_rcv(struct sk_buff *skb, struct udp_table *udptable,
int proto)
{
...
if (udp_lib_checksum_complete(skb))
goto csum_error;
__UDP6_INC_STATS(net, UDP_MIB_NOPORTS, proto == IPPROTO_UDPLITE);
icmpv6_send(skb, ICMPV6_DEST_UNREACH, ICMPV6_PORT_UNREACH, 0);
kfree_skb(skb);
return 0;
...
}
NDISC
NDISC 프로토콜은 같은 링크 상의 IPv6 노드가 서로의 존재를 탐색하거나, 서로의 L2 주소를 파악하거나, 라우터를 탐색하거나, 이웃 연결 가능 정보를 유지하기 위해 사용한다.
또한, 같은 링크 상의 이중 L3 주소가 존재하는 것을 방지하기 위하여 중복 주소 탐지(DAD) 기능이 추가됐다.
이 후의 내용은 Neighbour 포스트의 이웃 서브시스템과 ARP를 학습했다는 가정 하에 진행한다.
중복 주소 탐지 (DAD)
호스트가 부팅 후 주소를 설정하려고 할 때 우선 FE80으로 시작하는 Link-Local 주소를 생성한다.
이 주소는 임시 주소(IFA_F_TENTATIVE)인데, 이는 호스트가 ND 메시지로만 통신할 수 있음을 의미한다.
그런 다음 호스트는 addrconf_dad_start() 함수를 호출해 DAD 처리를 시작한다.
호스트는 이웃 의뢰(Neighbour Solicitation) DAD 메시지를 전송한다. 해당 메시지의 출발지 주소는 모두 0인 미지정 주소이며, 도착지 주소는 자신이 설정한 임시 주소이다.
지정된 시간 간격 내에 응답이 없으면 상태가 영구적(IFA_F_PERMANENT)으로 변경된다.
Optimistic DAD가 설정돼 있으면 (CONFIG_IPV6_OPTIMISTIC_DAD) DAD가 완료될 때까지 기다리지 않고 상대방과 통신할 수도 있다.
IPv6에 대한 이웃 테이블은 nd_tbl이라고 한다.
static const struct neigh_ops ndisc_generic_ops = {
.family = AF_INET6,
.solicit = ndisc_solicit,
.error_report = ndisc_error_report,
.output = neigh_resolve_output,
.connected_output = neigh_connected_output,
};
static const struct neigh_ops ndisc_hh_ops = {
.family = AF_INET6,
.solicit = ndisc_solicit,
.error_report = ndisc_error_report,
.output = neigh_resolve_output,
.connected_output = neigh_resolve_output,
};
static const struct neigh_ops ndisc_direct_ops = {
.family = AF_INET6,
.output = neigh_direct_output,
.connected_output = neigh_direct_output,
};
struct neigh_table nd_tbl = {
.family = AF_INET6,
.key_len = sizeof(struct in6_addr),
.protocol = cpu_to_be16(ETH_P_IPV6),
.hash = ndisc_hash,
.key_eq = ndisc_key_eq,
.constructor = ndisc_constructor,
.pconstructor = pndisc_constructor,
.pdestructor = pndisc_destructor,
.proxy_redo = pndisc_redo,
.is_multicast = ndisc_is_multicast,
.allow_add = ndisc_allow_add,
.id = "ndisc_cache",
.parms = {
.tbl = &nd_tbl,
.reachable_time = ND_REACHABLE_TIME,
.data = {
[NEIGH_VAR_MCAST_PROBES] = 3,
[NEIGH_VAR_UCAST_PROBES] = 3,
[NEIGH_VAR_RETRANS_TIME] = ND_RETRANS_TIMER,
[NEIGH_VAR_BASE_REACHABLE_TIME] = ND_REACHABLE_TIME,
[NEIGH_VAR_DELAY_PROBE_TIME] = 5 * HZ,
[NEIGH_VAR_GC_STALETIME] = 60 * HZ,
[NEIGH_VAR_QUEUE_LEN_BYTES] = SK_WMEM_MAX,
[NEIGH_VAR_PROXY_QLEN] = 64,
[NEIGH_VAR_ANYCAST_DELAY] = 1 * HZ,
[NEIGH_VAR_PROXY_DELAY] = (8 * HZ) / 10,
},
},
.gc_interval = 30 * HZ,
.gc_thresh1 = 128,
.gc_thresh2 = 512,
.gc_thresh3 = 1024,
};
일부 멤버는 보는 바와 같이 ARP 테이블 멤버와 동일하다.
이웃 탐색 메시지는 ICMPv6 메시지이므로, icmpv6_rcv() 함수로 처리된다.
ICMPv6 메시지 수신 챕터에서 본 바와 같이 그 중 NDISC 메시지는 ndisc_rcv() 함수를 호출하여 처리한다.
NDISC에는 ndisc_generic_ops, ndisc_hh_ops, ndisc_direct_ops 라는 세 가지 오퍼레이션 객체가 있다.
if (!dev->header_ops) {
neigh->nud_state = NUD_NOARP;
neigh->ops = &ndisc_direct_ops;
neigh->output = neigh_direct_output;
} else {
if (is_multicast) {
neigh->nud_state = NUD_NOARP;
ndisc_mc_map(addr, neigh->ha, dev, 1);
} else if (dev->flags&(IFF_NOARP|IFF_LOOPBACK)) {
neigh->nud_state = NUD_NOARP;
memcpy(neigh->ha, dev->dev_addr, dev->addr_len);
if (dev->flags&IFF_LOOPBACK)
neigh->type = RTN_LOCAL;
} else if (dev->flags&IFF_POINTOPOINT) {
neigh->nud_state = NUD_NOARP;
memcpy(neigh->ha, dev->broadcast, dev->addr_len);
}
if (dev->header_ops->cache)
neigh->ops = &ndisc_hh_ops;
else
neigh->ops = &ndisc_generic_ops;
if (neigh->nud_state&NUD_VALID)
neigh->output = neigh->ops->connected_output;
else
neigh->output = neigh->ops->output;
}
- net_device 객체의 header_ops가 NULL이면 neigh_ops 객체는
ndisc_direct_ops로 설정된다. - net_device 객체의 header_ops에 cache 멤버가 NULL이 아니면 neigh_ops 객체는
ndisc_hh_ops로 설정된다. - net_device 객체의 header_ops에 cache 멤버가 NULL이면 neigh_ops 객체는
ndisc_generic_ops로 설정된다.
NDISC 의뢰(Solicitation) 요청 송신
IPv4 Tx 경로와 유사하게 IPv6 Tx 경로에서도 ip6_finish_output2() 함수에서 neighbour 객체를 찾거나 생성하고, 해당 객체에 등록된 output 콜백을 호출한다.
static int ip6_finish_output2(struct net *net, struct sock *sk, struct sk_buff *skb)
{
...
neigh = __ipv6_neigh_lookup_noref(dst->dev, nexthop);
if (unlikely(!neigh))
neigh = __neigh_create(&nd_tbl, nexthop, dst->dev, false);
if (!IS_ERR(neigh)) {
sock_confirm_neigh(skb, neigh);
ret = neigh_output(neigh, skb, false);
rcu_read_unlock_bh();
return ret;
}
...
}
static inline int neigh_output(struct neighbour *n, struct sk_buff *skb,
bool skip_cache)
{
const struct hh_cache *hh = &n->hh;
if ((n->nud_state & NUD_CONNECTED) && hh->hh_len && !skip_cache)
return neigh_hh_output(hh, skb);
else
return n->output(n, skb);
}
n->output() 콜백은 neigh_resolve_output() 함수이며, 해당 함수에서부터 neigh_event_send() -> __neigh_event_send() -> neigh_probe() 함수를 호출한다.
neigh_probe() 함수에서는 neigh->ops->solicit 콜백을 호출하는데, 이는 ndisc_solicit() 함수이다. 해당 함수의 정의는 다음과 같다.
static void ndisc_solicit(struct neighbour *neigh, struct sk_buff *skb)
{
struct in6_addr *saddr = NULL;
struct in6_addr mcaddr;
struct net_device *dev = neigh->dev;
struct in6_addr *target = (struct in6_addr *)&neigh->primary_key;
int probes = atomic_read(&neigh->probes);
if (skb && ipv6_chk_addr_and_flags(dev_net(dev), &ipv6_hdr(skb)->saddr,
dev, false, 1,
IFA_F_TENTATIVE|IFA_F_OPTIMISTIC))
saddr = &ipv6_hdr(skb)->saddr;
probes -= NEIGH_VAR(neigh->parms, UCAST_PROBES);
if (probes < 0) {
if (!(neigh->nud_state & NUD_VALID)) {
ND_PRINTK(1, dbg,
"%s: trying to ucast probe in NUD_INVALID: %pI6\n",
__func__, target);
}
ndisc_send_ns(dev, target, target, saddr, 0);
} else if ((probes -= NEIGH_VAR(neigh->parms, APP_PROBES)) < 0) {
neigh_app_ns(neigh);
} else {
addrconf_addr_solict_mult(target, &mcaddr);
ndisc_send_ns(dev, target, &mcaddr, saddr, 0);
}
}
결국 ndisc_send_ns() 함수로 NDISC Node Solicitation 메시지를 송신한다.
ndisc_send_ns() 함수에서 의뢰 요청을 송신하려면 nd_msg 객체를 만들어야 한다.
struct nd_msg {
struct icmp6hdr icmph;
struct in6_addr target;
__u8 opt[];
};
의뢰 요청의 경우 ICMPv6 헤더 유형이 NDISC_NEIGHBOUR_SOLICITATION(135)으로 설정돼야 하고, 의뢰 응답의 경우 ICMPv6 헤더 유형이 NDISC_NEIGHBOUR_ADVERTISEMENT(136)으로 설정돼야 한다.
해당 포스트 초반부에 봤던 icmp6hdr 구조체의 생략된 부분에는 icmpv6_nd_advt라고 하는 구조체가 포함돼 있으며, 이 구조체에 override, solicited, router 플래그가 포함돼 있다.
struct icmp6hdr {
...
union {
__be32 un_data32[1];
__be16 un_data16[2];
__u8 un_data8[4];
...
struct icmpv6_nd_advt {
#if defined(__LITTLE_ENDIAN_BITFIELD)
__u32 reserved:5,
override:1,
solicited:1,
router:1,
reserved2:24;
#elif defined(__BIG_ENDIAN_BITFIELD)
__u32 router:1,
solicited:1,
override:1,
reserved:29;
#else
#error "Please fix <asm/byteorder.h>"
#endif
} u_nd_advt;
...
}
}
- 이웃 의뢰에 대한 응답 메시지를 전송할 때 solicited 플래그를 설정한다.
- 이웃 캐시 항목을 덮어쓰려면(L2 주소를 업데이트) override 플래그를 설정한다.
- 이웃 알림 메시지를 전송하는 호스트가 라우터면 router 플래그를 설정한다.
ndisc_send_ns() 함수의 정의는 다음과 같다.
void ndisc_send_ns(struct net_device *dev, const struct in6_addr *solicit,
const struct in6_addr *daddr, const struct in6_addr *saddr,
u64 nonce)
{
struct sk_buff *skb;
struct in6_addr addr_buf;
int inc_opt = dev->addr_len;
int optlen = 0;
struct nd_msg *msg;
if (!saddr) {
if (ipv6_get_lladdr(dev, &addr_buf,
(IFA_F_TENTATIVE|IFA_F_OPTIMISTIC)))
return;
saddr = &addr_buf;
}
if (ipv6_addr_any(saddr))
inc_opt = false;
if (inc_opt)
optlen += ndisc_opt_addr_space(dev,
NDISC_NEIGHBOUR_SOLICITATION);
if (nonce != 0)
optlen += 8;
skb = ndisc_alloc_skb(dev, sizeof(*msg) + optlen); // ICMPv6 헤더 생성
if (!skb)
return;
msg = skb_put(skb, sizeof(*msg)); // nd_msg 구조체 이용
*msg = (struct nd_msg) {
.icmph = {
.icmp6_type = NDISC_NEIGHBOUR_SOLICITATION, // 타입 지정
},
.target = *solicit,
};
if (inc_opt)
ndisc_fill_addr_option(skb, ND_OPT_SOURCE_LL_ADDR,
dev->dev_addr,
NDISC_NEIGHBOUR_SOLICITATION);
if (nonce != 0) {
u8 *opt = skb_put(skb, 8);
opt[0] = ND_OPT_NONCE;
opt[1] = 8 >> 3;
memcpy(opt + 2, &nonce, 6);
}
ndisc_send_skb(skb, daddr, saddr);
}
위 함수로 전송한 메시지는 ndisc_recv_ns() 함수에서 처리하며, 응답으로 ndisc_send_na 함수를 호출하여 NDISC Neighbour(Node) Advertisements 메시지를 송신한다.
NDISC 이웃 의뢰와 알림(Advertisements) 수신
앞서 말한 것과 같이, NDISC 수신 핸들러 함수는 ndisc_rcv() 함수이다.
해당 함수의 정의는 다음과 같다.
int ndisc_rcv(struct sk_buff *skb)
{
struct nd_msg *msg;
if (ndisc_suppress_frag_ndisc(skb))
return 0;
if (skb_linearize(skb))
return 0;
msg = (struct nd_msg *)skb_transport_header(skb);
__skb_push(skb, skb->data - skb_transport_header(skb));
if (ipv6_hdr(skb)->hop_limit != 255) { // RFC 4861에 따라 이웃 메시지의 홉은 255로 제한되어야 함
ND_PRINTK(2, warn, "NDISC: invalid hop-limit: %d\n",
ipv6_hdr(skb)->hop_limit);
return 0;
}
if (msg->icmph.icmp6_code != 0) { // RFC 4861에 따라 ICMPv6 코드는 0이어야 함
ND_PRINTK(2, warn, "NDISC: invalid ICMPv6 code: %d\n",
msg->icmph.icmp6_code);
return 0;
}
switch (msg->icmph.icmp6_type) { // NDISC 메시지 타입에 따른 처리
case NDISC_NEIGHBOUR_SOLICITATION:
memset(NEIGH_CB(skb), 0, sizeof(struct neighbour_cb));
ndisc_recv_ns(skb);
break;
case NDISC_NEIGHBOUR_ADVERTISEMENT:
ndisc_recv_na(skb);
break;
case NDISC_ROUTER_SOLICITATION:
ndisc_recv_rs(skb);
break;
case NDISC_ROUTER_ADVERTISEMENT:
ndisc_router_discovery(skb);
break;
case NDISC_REDIRECT:
ndisc_redirect_rcv(skb);
break;
}
return 0;
}
각 NDISC 메시지 타입에 따라 그에 맞는 핸들러 함수를 호출한다.
NDISC_NEIGHBOUR_SOLICITATION 메시지 핸들러는 ndisc_recv_ns() 함수이다.
int dad = ipv6_addr_any(saddr); 라인은 출발지 주소가 미지정 주소인지 확인한다. 미지정 주소라면 DAD 검사를 위한 패킷임을 알 수 있다.
이 후 여러 온전성 검사와 옵션 파싱을 수행한다. 이 후, 수신한 패킷이 DAD 패킷이었다면 Neighbour(Node) Advertisements 메시지를 송신하고 종료한다. (DAD 메시지를 수신한 것이라면, 중복 주소가 검출된 경우일 것이다.)
DAD가 아니라면 송신자의 L2 주소로 이웃 테이블을 업데이트 하고, NA 메시지를 송신한다.
if (dad) {
ndisc_send_na(dev, &in6addr_linklocal_allnodes, &msg->target,
!!is_router, false, (ifp != NULL), true);
goto out;
}
if (inc)
NEIGH_CACHE_STAT_INC(&nd_tbl, rcv_probes_mcast);
else
NEIGH_CACHE_STAT_INC(&nd_tbl, rcv_probes_ucast);
/*
* update / create cache entry
* for the source address
*/
neigh = __neigh_lookup(&nd_tbl, saddr, dev,
!inc || lladdr || !dev->addr_len);
if (neigh)
ndisc_update(dev, neigh, lladdr, NUD_STALE,
NEIGH_UPDATE_F_WEAK_OVERRIDE|
NEIGH_UPDATE_F_OVERRIDE,
NDISC_NEIGHBOUR_SOLICITATION, &ndopts);
if (neigh || !dev->header_ops) {
ndisc_send_na(dev, saddr, &msg->target, !!is_router,
true, (ifp != NULL && inc), inc);
if (neigh)
neigh_release(neigh);
}
NDISC_NEIGHBOUR_ADVERTISEMENT 메시지 핸들러는 ndisc_recv_na() 함수이다.
마찬가지로 여러 온전성 검사를 수행하고 옵션을 파싱한다.
이 후, 다음과 같이 이웃 서브시스템을 탐색하고 이웃 테이블을 업데이트한다.
neigh = neigh_lookup(&nd_tbl, &msg->target, dev);
if (neigh) {
u8 old_flags = neigh->flags;
struct net *net = dev_net(dev);
if (neigh->nud_state & NUD_FAILED)
goto out;
/*
* Don't update the neighbor cache entry on a proxy NA from
* ourselves because either the proxied node is off link or it
* has already sent a NA to us.
*/
if (lladdr && !memcmp(lladdr, dev->dev_addr, dev->addr_len) &&
net->ipv6.devconf_all->forwarding && net->ipv6.devconf_all->proxy_ndp &&
pneigh_lookup(&nd_tbl, net, &msg->target, dev, 0)) {
/* XXX: idev->cnf.proxy_ndp */
goto out;
}
// 수신한 메시지의 ICMPv6 헤더를 파싱하여 solicited, override, router 플래그를 확인
ndisc_update(dev, neigh, lladdr,
msg->icmph.icmp6_solicited ? NUD_REACHABLE : NUD_STALE, // solicited 플래그가 설정되어 있다면
NEIGH_UPDATE_F_WEAK_OVERRIDE| // NUD_REACHABLE 설정
(msg->icmph.icmp6_override ? NEIGH_UPDATE_F_OVERRIDE : 0)| // override 플래그가 설정되어 있다면
NEIGH_UPDATE_F_OVERRIDE_ISROUTER| // NEIGH_UPDATE_F_OVERRIDE 설정
(msg->icmph.icmp6_router ? NEIGH_UPDATE_F_ISROUTER : 0), // router 플래그가 설정되어 있다면
NDISC_NEIGHBOUR_ADVERTISEMENT, &ndopts); // NEIGH_UPDATE_F_ISROUTER 설정
if ((old_flags & ~neigh->flags) & NTF_ROUTER) {
/*
* Change: router to host
*/
rt6_clean_tohost(dev_net(dev), saddr);
}
이웃 테이블을 업데이트 하는 ndisc_update() 함수의 정의는 다음과 같다.
void ndisc_update(const struct net_device *dev, struct neighbour *neigh,
const u8 *lladdr, u8 new, u32 flags, u8 icmp6_type,
struct ndisc_options *ndopts)
{
neigh_update(neigh, lladdr, new, flags, 0);
/* report ndisc ops about neighbour update */
ndisc_ops_update(dev, neigh, flags, icmp6_type, ndopts);
}
예제
새로운 ICMPv6 타입과 그에 대한 핸들러 함수를 정의하고, echo 메시지에 대한 응답으로 해당 타입의 ICMP 메시지를 송신하여 핸들러 함수가 호출되는 것을 확인한다.
해당 예제는 송신측과 수신측 호스트에 모두 아래 수정된 커널 내용이 적용되어야 한다.
linux/include/uapi/linux/icmpv6.h
116 라인에 다음과 같이 새로운 메시지 타입을 정의한다.
#define ICMPV6_DHAAD_REQUEST 144
#define ICMPV6_DHAAD_REPLY 145
#define ICMPV6_MOBILE_PREFIX_SOL 146
#define ICMPV6_MOBILE_PREFIX_ADV 147
#define ICMPV6_MRDISC_ADV 151
#define ICMPV6_PR0GR4M 152 // 추가된 라인
#define ICMPV6_MSG_MAX 255
linux/net/ipv6/icmp.c
헤더 파일을 삽입한다.
#include "ip_km.h"
850 라인 부근(icmpv6_rcv 함수 위)에 다음 함수를 추가한다.
static void pr0gr4m_rcv(struct sk_buff *skb)
{ // 새로운 ICMPv6 타입에 대한 핸들러 함수
// 알람 문구를 출력하고, skb 내용을 출력한다.
printk("[pr0gr4m] receive icmpv6 message\n");
print_skb(skb);
}
/*
* Handle icmp messages
*/
static int icmpv6_rcv(struct sk_buff *skb)
icmpv6_rcv() 함수의 switch 문을 다음과 같이 수정한다.
switch (type) {
case ICMPV6_ECHO_REQUEST:
if (!net->ipv6.sysctl.icmpv6_echo_ignore_all)
icmpv6_echo_reply(skb);
// 추가된 라인, ECHO_REQUEST 메시지를 수신하면
// echo_reply 함수 호출 후에 새로 정의한 타입의
// icmp 메시지를 송신한다.
icmpv6_send(skb, ICMPV6_PR0GR4M, 0, 8);
break;
case ICMPV6_ECHO_REPLY:
success = ping_rcv(skb);
break;
case ICMPV6_PKT_TOOBIG:
/* BUGGG_FUTURE: if packet contains rthdr, we cannot update
standard destination cache. Seems, only "advanced"
destination cache will allow to solve this problem
--ANK (980726)
*/
if (!pskb_may_pull(skb, sizeof(struct ipv6hdr)))
goto discard_it;
hdr = icmp6_hdr(skb);
/* to notify */
fallthrough;
case ICMPV6_DEST_UNREACH:
case ICMPV6_TIME_EXCEED:
case ICMPV6_PARAMPROB:
icmpv6_notify(skb, type, hdr->icmp6_code, hdr->icmp6_mtu);
break;
case NDISC_ROUTER_SOLICITATION:
case NDISC_ROUTER_ADVERTISEMENT:
case NDISC_NEIGHBOUR_SOLICITATION:
case NDISC_NEIGHBOUR_ADVERTISEMENT:
case NDISC_REDIRECT:
ndisc_rcv(skb);
break;
case ICMPV6_MGM_QUERY:
igmp6_event_query(skb);
break;
case ICMPV6_MGM_REPORT:
igmp6_event_report(skb);
break;
case ICMPV6_MGM_REDUCTION:
case ICMPV6_NI_QUERY:
case ICMPV6_NI_REPLY:
case ICMPV6_MLD2_REPORT:
case ICMPV6_DHAAD_REQUEST:
case ICMPV6_DHAAD_REPLY:
case ICMPV6_MOBILE_PREFIX_SOL:
case ICMPV6_MOBILE_PREFIX_ADV:
break;
case ICMPV6_PR0GR4M:
// 추가된 라인, 새로 정의된 타입의 메시지를 수신하면
// 새로 정의한 핸들러 함수를 호출한다.
pr0gr4m_rcv(skb);
break;
default:
/* informational */
if (type & ICMPV6_INFOMSG_MASK)
break;
net_dbg_ratelimited("icmpv6: msg of unknown type [%pI6c > %pI6c]\n",
saddr, daddr);
/*
* error of unknown type.
* must pass to upper level
*/
icmpv6_notify(skb, type, hdr->icmp6_code, hdr->icmp6_mtu);
}
빌드 및 결과
linux root 디렉토리에서 다음과 같이 빌드한다.
$ make -j8
$ sudo make install
이 후 다음과 같이 ping6 명령으로 메시지를 송신하고 dmesg에서 커널 메시지를 확인한다.
$ ping6 <수신 호스트 IPv6 주소>
$ dmesg
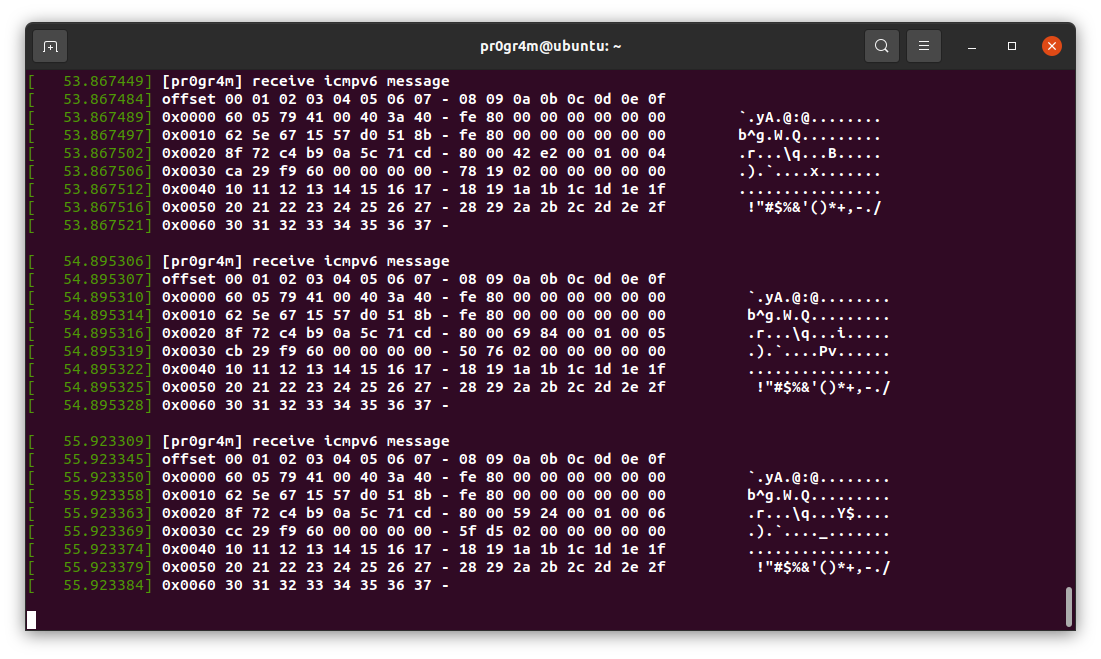
정상적으로 새로 정의한 메시지 타입을 파싱하여 핸들러를 호출한 것을 확인할 수 있다.