Linux Kernel SKB
해당 포스트에서는 sk_buff 구조체에 대하여 설명합니다.
struct sk_buff
패킷을 수신하면 네트워크 장치 드라이버가 netdev_alloc_skb 함수를 호출하여 sk_buff 구조체를 할당한다.
패킷이 drop되는 경우에는 kfree_skb 함수를 호출하여 할당을 해제한다.
다음은 sk_buff 구조체의 정의이며, 이 중 주요 멤버를 설명한다.
/**
* struct sk_buff - socket buffer
* @next: Next buffer in list
* @prev: Previous buffer in list
* @tstamp: Time we arrived/left
* @skb_mstamp_ns: (aka @tstamp) earliest departure time; start point
* for retransmit timer
* @rbnode: RB tree node, alternative to next/prev for netem/tcp
* @list: queue head
* @sk: Socket we are owned by
* @ip_defrag_offset: (aka @sk) alternate use of @sk, used in
* fragmentation management
* @dev: Device we arrived on/are leaving by
* @dev_scratch: (aka @dev) alternate use of @dev when @dev would be %NULL
* @cb: Control buffer. Free for use by every layer. Put private vars here
* @_skb_refdst: destination entry (with norefcount bit)
* @sp: the security path, used for xfrm
* @len: Length of actual data
* @data_len: Data length
* @mac_len: Length of link layer header
* @hdr_len: writable header length of cloned skb
* @csum: Checksum (must include start/offset pair)
* @csum_start: Offset from skb->head where checksumming should start
* @csum_offset: Offset from csum_start where checksum should be stored
* @priority: Packet queueing priority
* @ignore_df: allow local fragmentation
* @cloned: Head may be cloned (check refcnt to be sure)
* @ip_summed: Driver fed us an IP checksum
* @nohdr: Payload reference only, must not modify header
* @pkt_type: Packet class
* @fclone: skbuff clone status
* @ipvs_property: skbuff is owned by ipvs
* @inner_protocol_type: whether the inner protocol is
* ENCAP_TYPE_ETHER or ENCAP_TYPE_IPPROTO
* @remcsum_offload: remote checksum offload is enabled
* @offload_fwd_mark: Packet was L2-forwarded in hardware
* @offload_l3_fwd_mark: Packet was L3-forwarded in hardware
* @tc_skip_classify: do not classify packet. set by IFB device
* @tc_at_ingress: used within tc_classify to distinguish in/egress
* @redirected: packet was redirected by packet classifier
* @from_ingress: packet was redirected from the ingress path
* @peeked: this packet has been seen already, so stats have been
* done for it, don't do them again
* @nf_trace: netfilter packet trace flag
* @protocol: Packet protocol from driver
* @destructor: Destruct function
* @tcp_tsorted_anchor: list structure for TCP (tp->tsorted_sent_queue)
* @_sk_redir: socket redirection information for skmsg
* @_nfct: Associated connection, if any (with nfctinfo bits)
* @nf_bridge: Saved data about a bridged frame - see br_netfilter.c
* @skb_iif: ifindex of device we arrived on
* @tc_index: Traffic control index
* @hash: the packet hash
* @queue_mapping: Queue mapping for multiqueue devices
* @head_frag: skb was allocated from page fragments,
* not allocated by kmalloc() or vmalloc().
* @pfmemalloc: skbuff was allocated from PFMEMALLOC reserves
* @active_extensions: active extensions (skb_ext_id types)
* @ndisc_nodetype: router type (from link layer)
* @ooo_okay: allow the mapping of a socket to a queue to be changed
* @l4_hash: indicate hash is a canonical 4-tuple hash over transport
* ports.
* @sw_hash: indicates hash was computed in software stack
* @wifi_acked_valid: wifi_acked was set
* @wifi_acked: whether frame was acked on wifi or not
* @no_fcs: Request NIC to treat last 4 bytes as Ethernet FCS
* @encapsulation: indicates the inner headers in the skbuff are valid
* @encap_hdr_csum: software checksum is needed
* @csum_valid: checksum is already valid
* @csum_not_inet: use CRC32c to resolve CHECKSUM_PARTIAL
* @csum_complete_sw: checksum was completed by software
* @csum_level: indicates the number of consecutive checksums found in
* the packet minus one that have been verified as
* CHECKSUM_UNNECESSARY (max 3)
* @dst_pending_confirm: need to confirm neighbour
* @decrypted: Decrypted SKB
* @napi_id: id of the NAPI struct this skb came from
* @sender_cpu: (aka @napi_id) source CPU in XPS
* @secmark: security marking
* @mark: Generic packet mark
* @reserved_tailroom: (aka @mark) number of bytes of free space available
* at the tail of an sk_buff
* @vlan_present: VLAN tag is present
* @vlan_proto: vlan encapsulation protocol
* @vlan_tci: vlan tag control information
* @inner_protocol: Protocol (encapsulation)
* @inner_ipproto: (aka @inner_protocol) stores ipproto when
* skb->inner_protocol_type == ENCAP_TYPE_IPPROTO;
* @inner_transport_header: Inner transport layer header (encapsulation)
* @inner_network_header: Network layer header (encapsulation)
* @inner_mac_header: Link layer header (encapsulation)
* @transport_header: Transport layer header
* @network_header: Network layer header
* @mac_header: Link layer header
* @kcov_handle: KCOV remote handle for remote coverage collection
* @tail: Tail pointer
* @end: End pointer
* @head: Head of buffer
* @data: Data head pointer
* @truesize: Buffer size
* @users: User count - see {datagram,tcp}.c
* @extensions: allocated extensions, valid if active_extensions is nonzero
*/
struct sk_buff {
union {
struct {
/* These two members must be first. */
struct sk_buff *next;
struct sk_buff *prev;
union {
struct net_device *dev;
/* Some protocols might use this space to store information,
* while device pointer would be NULL.
* UDP receive path is one user.
*/
unsigned long dev_scratch;
};
};
struct rb_node rbnode; /* used in netem, ip4 defrag, and tcp stack */
struct list_head list;
};
union {
struct sock *sk;
int ip_defrag_offset;
};
union {
ktime_t tstamp;
u64 skb_mstamp_ns; /* earliest departure time */
};
/*
* This is the control buffer. It is free to use for every
* layer. Please put your private variables there. If you
* want to keep them across layers you have to do a skb_clone()
* first. This is owned by whoever has the skb queued ATM.
*/
char cb[48] __aligned(8);
union {
struct {
unsigned long _skb_refdst;
void (*destructor)(struct sk_buff *skb);
};
struct list_head tcp_tsorted_anchor;
#ifdef CONFIG_NET_SOCK_MSG
unsigned long _sk_redir;
#endif
};
#if defined(CONFIG_NF_CONNTRACK) || defined(CONFIG_NF_CONNTRACK_MODULE)
unsigned long _nfct;
#endif
unsigned int len,
data_len;
__u16 mac_len,
hdr_len;
/* Following fields are _not_ copied in __copy_skb_header()
* Note that queue_mapping is here mostly to fill a hole.
*/
__u16 queue_mapping;
/* if you move cloned around you also must adapt those constants */
#ifdef __BIG_ENDIAN_BITFIELD
#define CLONED_MASK (1 << 7)
#else
#define CLONED_MASK 1
#endif
#define CLONED_OFFSET() offsetof(struct sk_buff, __cloned_offset)
/* private: */
__u8 __cloned_offset[0];
/* public: */
__u8 cloned:1,
nohdr:1,
fclone:2,
peeked:1,
head_frag:1,
pfmemalloc:1;
#ifdef CONFIG_SKB_EXTENSIONS
__u8 active_extensions;
#endif
/* fields enclosed in headers_start/headers_end are copied
* using a single memcpy() in __copy_skb_header()
*/
/* private: */
__u32 headers_start[0];
/* public: */
/* if you move pkt_type around you also must adapt those constants */
#ifdef __BIG_ENDIAN_BITFIELD
#define PKT_TYPE_MAX (7 << 5)
#else
#define PKT_TYPE_MAX 7
#endif
#define PKT_TYPE_OFFSET() offsetof(struct sk_buff, __pkt_type_offset)
/* private: */
__u8 __pkt_type_offset[0];
/* public: */
__u8 pkt_type:3;
__u8 ignore_df:1;
__u8 nf_trace:1;
__u8 ip_summed:2;
__u8 ooo_okay:1;
__u8 l4_hash:1;
__u8 sw_hash:1;
__u8 wifi_acked_valid:1;
__u8 wifi_acked:1;
__u8 no_fcs:1;
/* Indicates the inner headers are valid in the skbuff. */
__u8 encapsulation:1;
__u8 encap_hdr_csum:1;
__u8 csum_valid:1;
#ifdef __BIG_ENDIAN_BITFIELD
#define PKT_VLAN_PRESENT_BIT 7
#else
#define PKT_VLAN_PRESENT_BIT 0
#endif
#define PKT_VLAN_PRESENT_OFFSET() offsetof(struct sk_buff, __pkt_vlan_present_offset)
/* private: */
__u8 __pkt_vlan_present_offset[0];
/* public: */
__u8 vlan_present:1;
__u8 csum_complete_sw:1;
__u8 csum_level:2;
__u8 csum_not_inet:1;
__u8 dst_pending_confirm:1;
#ifdef CONFIG_IPV6_NDISC_NODETYPE
__u8 ndisc_nodetype:2;
#endif
__u8 ipvs_property:1;
__u8 inner_protocol_type:1;
__u8 remcsum_offload:1;
#ifdef CONFIG_NET_SWITCHDEV
__u8 offload_fwd_mark:1;
__u8 offload_l3_fwd_mark:1;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_NET_CLS_ACT
__u8 tc_skip_classify:1;
__u8 tc_at_ingress:1;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_NET_REDIRECT
__u8 redirected:1;
__u8 from_ingress:1;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_TLS_DEVICE
__u8 decrypted:1;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_NET_SCHED
__u16 tc_index; /* traffic control index */
#endif
union {
__wsum csum;
struct {
__u16 csum_start;
__u16 csum_offset;
};
};
__u32 priority;
int skb_iif;
__u32 hash;
__be16 vlan_proto;
__u16 vlan_tci;
#if defined(CONFIG_NET_RX_BUSY_POLL) || defined(CONFIG_XPS)
union {
unsigned int napi_id;
unsigned int sender_cpu;
};
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_NETWORK_SECMARK
__u32 secmark;
#endif
union {
__u32 mark;
__u32 reserved_tailroom;
};
union {
__be16 inner_protocol;
__u8 inner_ipproto;
};
__u16 inner_transport_header;
__u16 inner_network_header;
__u16 inner_mac_header;
__be16 protocol;
__u16 transport_header;
__u16 network_header;
__u16 mac_header;
#ifdef CONFIG_KCOV
u64 kcov_handle;
#endif
/* private: */
__u32 headers_end[0];
/* public: */
/* These elements must be at the end, see alloc_skb() for details. */
sk_buff_data_t tail;
sk_buff_data_t end;
unsigned char *head,
*data;
unsigned int truesize;
refcount_t users;
#ifdef CONFIG_SKB_EXTENSIONS
/* only useable after checking ->active_extensions != 0 */
struct skb_ext *extensions;
#endif
};
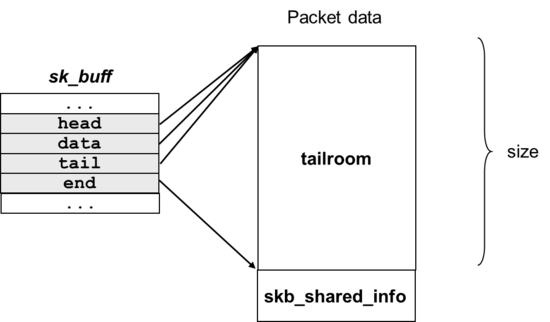
- unsigned char *data : 데이터의 head 포인터
- unsigned char *head : 버퍼의 head 포인터
- sk_buff_data_t tail : 데이터의 tail 포인터
- sk_buff_data_t end : 버퍼의 end 포인터로 tail이 end를 초과할 수 없다.
- struct net_device *dev : sk_buff와 연관된 네트워크 인터페이스 장치를 나타내는 net_device 객체이다.
- sturct sock *sk : sk_buff를 소유한 socket이다. 포워딩되는 패킷의 sk는 NULL이다.
- ktime_t tstamp : 패킷의 도착 타임스탬프. 다음과 같은 헬퍼 함수가 있다.
ktime_t skb_get_ktime(const struct sk_buff *skb): skb의 tstamp를 반환한다.void skb_get_timestamp(const struct sk_buff *skb, struct __kernel_old_timeval *stamp): skb로부터 timestamp를 구하는 legacy 함수이다.void skb_get_new_timestamp(const struct sk_buff *skb, struct __kernel_sock_timeval *stamp): struct timespec64 구조체에 skb의 timestamp를 저장한다.void skb_get_new_timestampns(const struct sk_buff *skb, struct __kernel_sock_timeval *stamp): skb_get_new_timestamp의 nanosecond 버전void __net_timestamp(struct sk_buff *skb): skb 구조체에 ktime_get_real() 함수의 반환 값으로 tstamp를 설정한다.
- char cb[48] : 여러 계층에서 자유롭게 사용할 수 있는 control buffer이다. 외부에 공개하지 않을 정보를 저장하는데 사용한다.
- unsigned long _skb_refdst : 목적지 항목(dst_entry)의 주소이다. dst_entry 구조체는 특정 목적지에 대한 라우팅 항목을 나타내며, 각 송수신 패킷은 라우팅 테이블에서 탐색을 수행한다. 다음과 같은 헬퍼 함수가 있다.
void skb_dst_set(struct sk_buff *skb, struct dst_entry *dst): skb에 dst를 설정한다. 이 때 참조를 dst에서 취하고 dst_release() 함수를 통해 release 한다고 가정한다.void skb_dst_set_noref(struct sk_buff *skb, struct dst_entry *dst): skb에 dst를 설정한다. 이 때 dst에서 참조를 취하지 않는다고 가정한다. refdst_drop 함수에서 dst에 대해 dst_release() 함수를 호출하지 않을 것이다.
- void (*destructor)(struct sk_buff *skb) : kfree_skb() 함수를 호출하여 skb 객체를 해제할 때 호출되는 콜백 함수
- unsigned int len : 패킷 바이트의 전체 길이
- unsigned int data_len : 데이터의 길이
- __u16 mac_len : MAC 헤더의 길이
- __u16 hdr_len : clone된 skb의 writable한 헤더 길이
- __u8 pkt_type:3 : 패킷의 클래스다. 이더넷의 경우 헤더의 목적지 MAC 주소에 의해 좌우되며, 주로 eth_type_trans() 함수로 결정한다.
- 본인 호스트 : PACKET_HOST
- 브로드캐스트 : PACKET_BROADCAST
- 멀티캐스트 : PACKET_MULTICAST
- 다른 호스트 : PACKET_OTHERHOST
- 루프백 : PAKCET_LOOPBACK
- __wsum csum : 체크섬
- __u32 priority : 패킷의 큐 우선순위.
- __u8 cloned:1 : 패킷이 clone 함수로 복제되면 해당 필드는 cloned 객체와 원본 객체 모두 1로 설정된다. 데이터 영역은 복제본과 원본 객체가 공유한다.
- __u8 peeked:1 : 이미 확인되어 통계 작업이 이루어졌는지에 대한 플래그. 설정되었다면 통계 작업을 다시 수행하지 않는다.
- __be16 protocol : 드라이버에 의해 설정된 패킷의 protocol. 이더넷이라면 eth_type_trans() 함수에 의해 rx 경로에서 ETH_P_IP로 초기화된다.
- __u32 hash : 패킷의 hash로 IP 헤더의 출발지, 목적지 주소와 전송 헤더의 포트에 따라 계산된다. SMP로 작동 시 동일 flow의 패킷이 같은 CPU에서 처리되는 것을 보장하는 데 사용하여 캐시 미스를 줄인다.
- __u32 mark : skb를 객체 식별을 위한 mark이다. 예를 들어 iptables 명령으로 다음과 같이 설정할 수 있다.
iptables -A PREROUTING -t mangle -i eth1 -j MARK --set-mark 0x1234: 탐색을 수행하기 전 eth1의 수신 트래픽을 대상으로 모든 skb 객체의 mark 필드에 0x1234를 할당한다.
- __u16 transport_header : transport layer (L4) 헤더이다. 헬퍼 함수는 다음과 같다.
unsigned char *skb_transport_header(const struct sk_buff *skb): skb의 transport header를 반환한다.bool skb_transport_header_was_set(const struct sk_buff *skb): skb의 transport header가 세팅되어 있다면 1을 반환한다.
- __u16 network_header : network layer (L3) 헤더이다. 헬퍼 함수는 다음과 같다.
unsigned char *skb_network_header(const struct sk_buff *skb): skb의 network header를 반환한다.void skb_reset_network_header(struct sk_buff *skb): skb의 network header를 다시 계산한다.void skb_set_network_header(strut sk_buff *skb, const int offset): skb의 network header를 offset을 이용하여 세팅한다.
- __u16 mac_header : datalink layer (L2) 헤더이다. 헬퍼 함수는 다음과 같다.
unsigned char *skb_mac_header(const struct sk_buff *skb): skb의 datalink header를 반환한다.int skb_mac_header_was_set(const struct sk_buff *skb): skb의 datalink header가 세팅되어 있다면 1을 반환한다.int skb_mac_offset(const struct sk_buff *skb): skb의 datalink header의 offset을 반환한다.u32 skb_mac_header_len(const struct sk_buff *skb): skb의 datalink header의 길이를 반환한다.
- unsigned int truesize : skb에 할당된 전체 메모리 크기
- refcount_t users : 해당 skb 객체의 참조 카운터이다. 1로 초기화되며, skb_get() 함수로 증가하고, kfree_skb() 함수나 consume_skb() 함수로 감소한다. 값이 0에 도달하면 skb 객체가 해제된다. 헬퍼 함수는 다음과 같다.
struct sk_buff *skb_get(struct sk_buff *skb): 참조 카운터를 1 증가시킨다.int skb_shared(const struct sk_buff *skb): 참조 카운터가 1이 아니면 true를 반환한다.sk_buff *skb_share_check(struct sk_buff *skb, gfp_t pri): 버퍼가 공유되지 않으면 원래 버퍼가 반환된다. 버퍼가 공유되면 버퍼는 복제되고, 이 전 복사본은 참조를 폐기하여 새로운 복제본은 단일 참조로 반환된다. 인터럽트 컨텍스트나 스핀락에서 호출되면 pri 매개변수는 GFP_ATOMIC이어야 한다.void consume_skb(struct sk_buff *skb): kfree_skb 함수를 호출한다.bool skb_unref(struct sk_buff *skb): skb의 레퍼런스 카운터를 1 감소하고, 감소한 카운터가 0이라면 true를 아니라면 false를 반환한다.void kfree_skb(struct sk_buff *skb): skb_unref를 호출하여 레퍼런스 카운터를 감소시키고, 카운터가 0이라면 skb 객체를 해제한다.
sk_buff 컨트롤 함수
다음 링크를 참고한다.
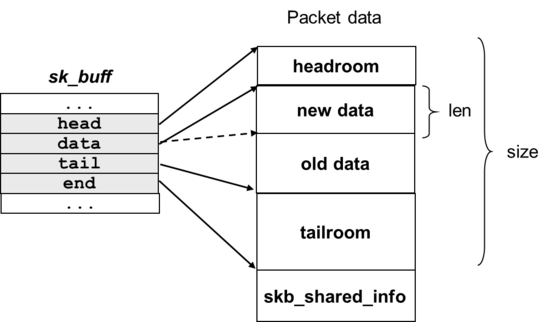
struct sk_buff *alloc_skb(unsigned int size, gfp_t priority): sk_buff 객체를 할당한다.void *skb_put(struct sk_buff *skb, unsigned int len): 버퍼에 데이터를 추가한다. skb 객체의 버퍼의 data 영역의 길이를 len만큼 확장한다. 해당 확장이 전체 버퍼 사이즈를 초과하면 (즉, tail 포인터가 end 포인터를 넘어서면) kernel panic이 발생한다. 반환 값은 extra data의 첫 바이트이다.void *skb_push(struct sk_buff *skb, unsigned int len): 버퍼의 시작부에 데이터를 추가한다. skb 객체의 기존 data 포인터가 len만큼 감소하고, skb의 크기를 len만큼 증가시킨다. 반환 값은 extra data의 첫 번째 바이트이다.void *skb_pull(struct sk_buff *skb, unsigned int len): 버퍼의 시작부에서 데이터를 제거한다. skb 객체의 크기를 len만큼 감소시키고, data 포인터를 len만큼 증가시킨다. skb_push 함수와 정반대의 함수이다. 반환 값은 버퍼의 next data의 포인터이다. data를 pull 한 이 후 push하면 old data는 overwrite될 것이다.void skb_reserve(struct sk_buff *skb, int len): skb 객체의 data와 tail을 len만큼 증가하여 (해당 작업은 tailroom을 감소시킨다) 빈 skb 객체의 headroom을 증가시킨다. 비어있는 버퍼에 대해서만 해당 함수를 사용할 수 있다.
다음은 eth_type_trans 함수와 ip_build_and_send_pkt 함수의 정의이다.
skb 객체의 내용을 덮어쓰거나 추가하는 것을 볼 수 있다.
/**
* eth_type_trans - determine the packet's protocol ID.
* @skb: received socket data
* @dev: receiving network device
*
* The rule here is that we
* assume 802.3 if the type field is short enough to be a length.
* This is normal practice and works for any 'now in use' protocol.
*/
__be16 eth_type_trans(struct sk_buff *skb, struct net_device *dev)
{
unsigned short _service_access_point;
const unsigned short *sap;
const struct ethhdr *eth;
skb->dev = dev;
skb_reset_mac_header(skb);
eth = (struct ethhdr *)skb->data;
skb_pull_inline(skb, ETH_HLEN);
if (unlikely(!ether_addr_equal_64bits(eth->h_dest,
dev->dev_addr))) {
if (unlikely(is_multicast_ether_addr_64bits(eth->h_dest))) {
if (ether_addr_equal_64bits(eth->h_dest, dev->broadcast))
skb->pkt_type = PACKET_BROADCAST;
else
skb->pkt_type = PACKET_MULTICAST;
} else {
skb->pkt_type = PACKET_OTHERHOST;
}
}
/*
* Some variants of DSA tagging don't have an ethertype field
* at all, so we check here whether one of those tagging
* variants has been configured on the receiving interface,
* and if so, set skb->protocol without looking at the packet.
* The DSA tagging protocol may be able to decode some but not all
* traffic (for example only for management). In that case give it the
* option to filter the packets from which it can decode source port
* information.
*/
if (unlikely(netdev_uses_dsa(dev)) && dsa_can_decode(skb, dev))
return htons(ETH_P_XDSA);
if (likely(eth_proto_is_802_3(eth->h_proto)))
return eth->h_proto;
/*
* This is a magic hack to spot IPX packets. Older Novell breaks
* the protocol design and runs IPX over 802.3 without an 802.2 LLC
* layer. We look for FFFF which isn't a used 802.2 SSAP/DSAP. This
* won't work for fault tolerant netware but does for the rest.
*/
sap = skb_header_pointer(skb, 0, sizeof(*sap), &_service_access_point);
if (sap && *sap == 0xFFFF)
return htons(ETH_P_802_3);
/*
* Real 802.2 LLC
*/
return htons(ETH_P_802_2);
}
/*
* Add an ip header to a skbuff and send it out.
*
*/
int ip_build_and_send_pkt(struct sk_buff *skb, const struct sock *sk,
__be32 saddr, __be32 daddr, struct ip_options_rcu *opt,
u8 tos)
{
struct inet_sock *inet = inet_sk(sk);
struct rtable *rt = skb_rtable(skb);
struct net *net = sock_net(sk);
struct iphdr *iph;
/* Build the IP header. */
skb_push(skb, sizeof(struct iphdr) + (opt ? opt->opt.optlen : 0));
skb_reset_network_header(skb);
iph = ip_hdr(skb);
iph->version = 4;
iph->ihl = 5;
iph->tos = tos;
iph->ttl = ip_select_ttl(inet, &rt->dst);
iph->daddr = (opt && opt->opt.srr ? opt->opt.faddr : daddr);
iph->saddr = saddr;
iph->protocol = sk->sk_protocol;
if (ip_dont_fragment(sk, &rt->dst)) {
iph->frag_off = htons(IP_DF);
iph->id = 0;
} else {
iph->frag_off = 0;
__ip_select_ident(net, iph, 1);
}
if (opt && opt->opt.optlen) {
iph->ihl += opt->opt.optlen>>2;
ip_options_build(skb, &opt->opt, daddr, rt, 0);
}
skb->priority = sk->sk_priority;
if (!skb->mark)
skb->mark = sk->sk_mark;
/* Send it out. */
return ip_local_out(net, skb->sk, skb);
}
example
ICMP, IP, ethernet 헤더와 payload를 추가하여 전송하는 경우
sender
struct skbuff *skb = skb_alloc(full_len, GFP_KERNEL);
/* icmp_hlen, ip_hlen and payload_size should be known */
int header_size = icmp_hlen + ip_hlen;
/* reserve headroom */
skb_reserve(skb, header_size);
/* payload */
unsigned char *data = skb_put(skb, payload_size);
memcpy(data, orig_skb->data, payload_size);
struct icmphdr *icmph = skb_push(skb, icmp_hlen);
/* set up icmp header here */
struct iphdr *iph = skb_push(skb, ip_hlen);
/* set up ip header here */
/*
* This function sets up the ethernet header,
* destination address addr, source address myaddr
*/
dev_hard_header(skb, dev, ETH_P_IP, addr, myaddr, dev->addr_len);